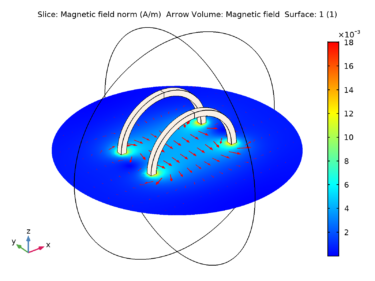
Computing the spatial derivative of the magnetic field or magnetic flux density is useful in areas such as radiology, magnetophoresis, particle accelerators, and geophysics. One of the most important use cases is the design of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machines, where it is necessary to analyze not only the field strength but also the spatial variation of the field. Read more